
Security researchers at Tenable Cloud Research have disclosed a significant supply chain vulnerability dubbed "GerriScary" that exposed at least 18 major Google projects to unauthorised code injection attacks.
The vulnerability, which has been remediated, affected critical software, including ChromiumOS (assigned CVE-2025-1568), Chromium browser, Google's Bazel build system, and the Dart programming language.
GerriScary exploited fundamental misconfigurations in Google's Gerrit code-review platform, which serves as the collaborative hub for managing code changes across Google's open-source projects. The vulnerability combined three critical components to create a sophisticated attack chain that could inject malicious code without human intervention.
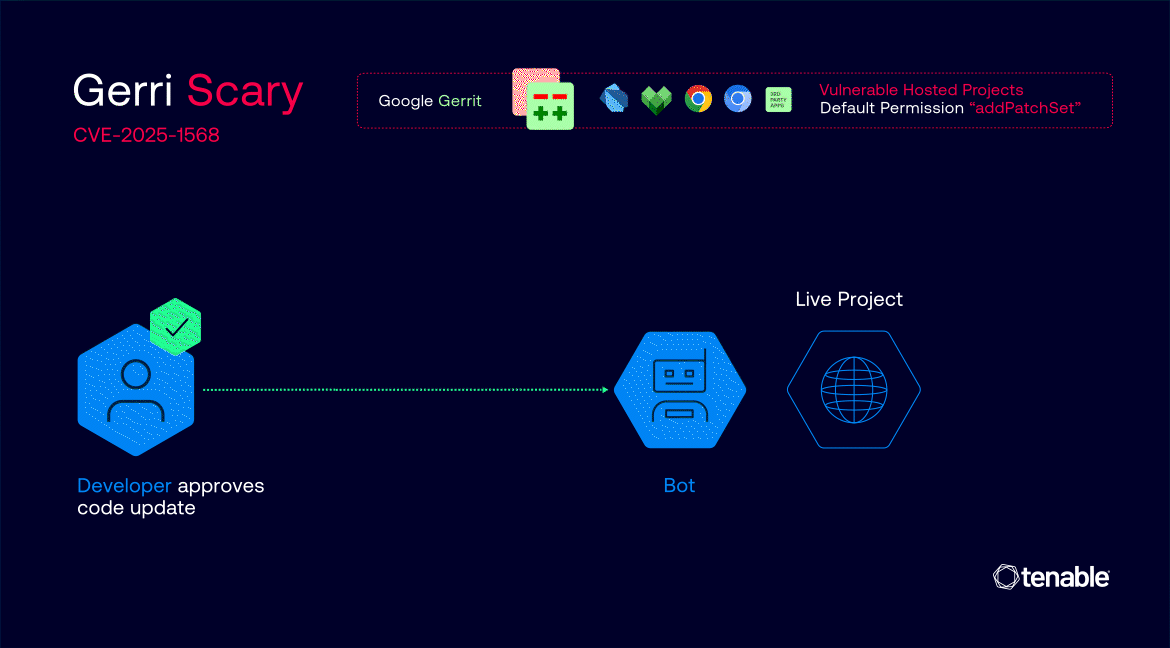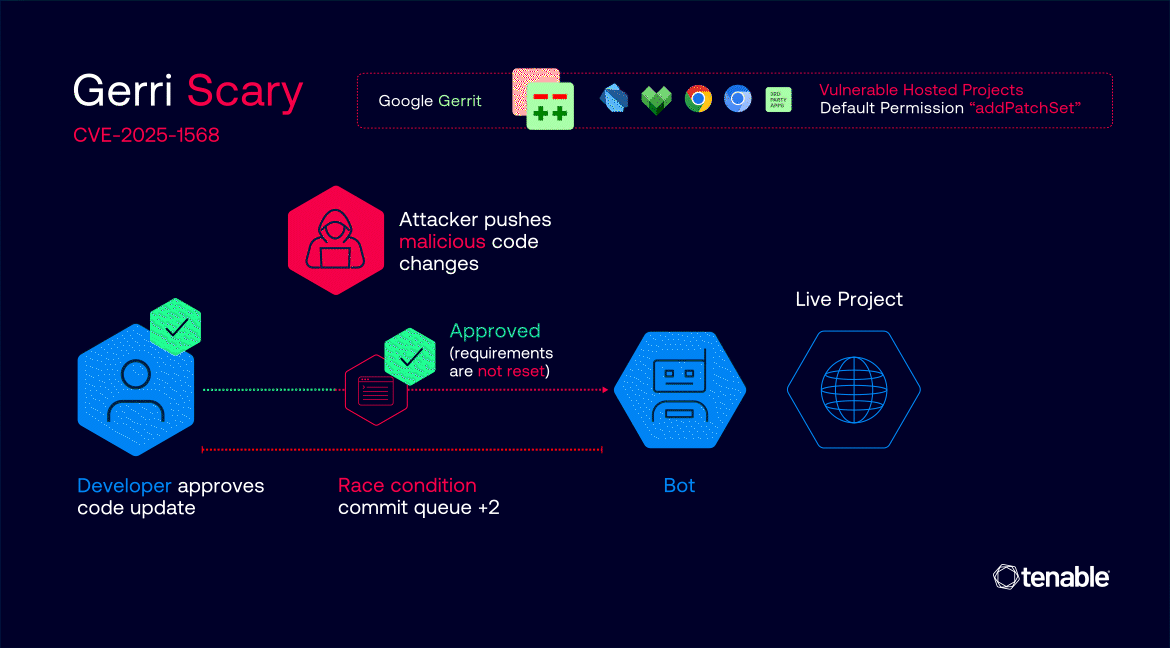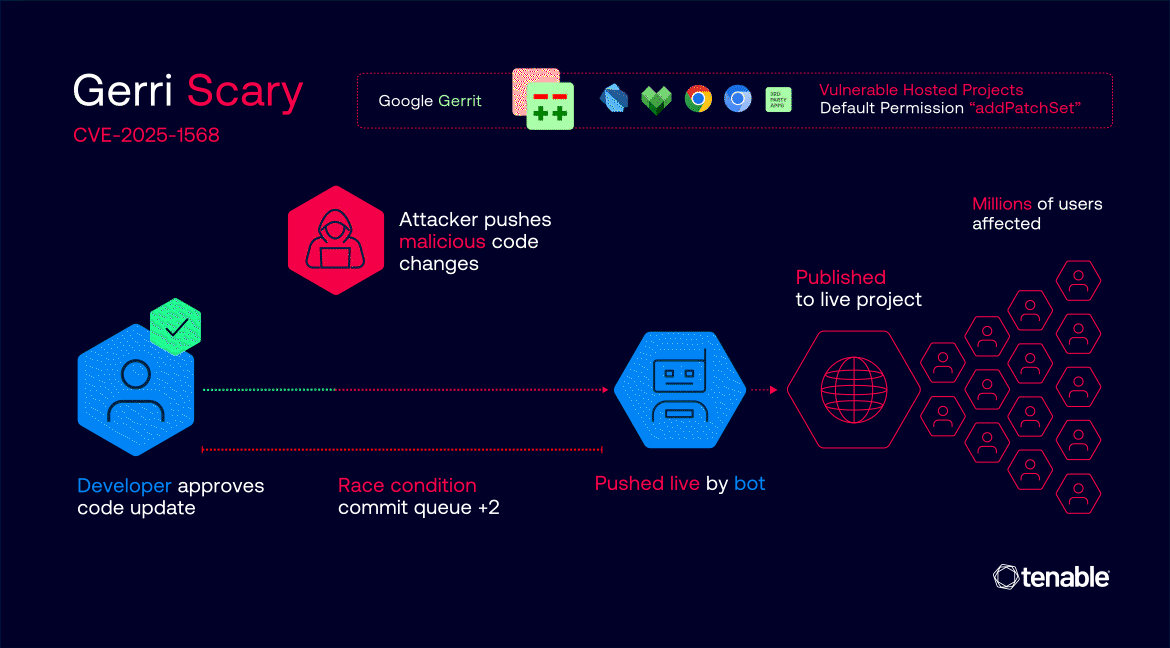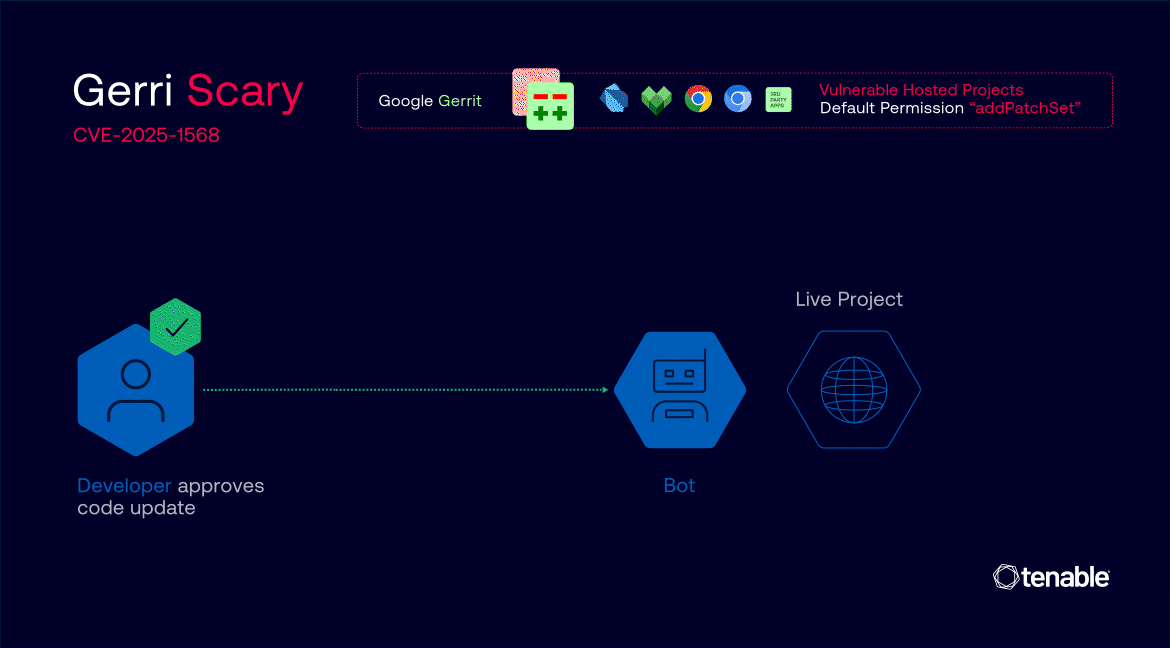
The attack leveraged Gerrit's default "addPatchSet" permission, which allows any registered user to modify existing code change proposals. This seemingly benign feature became dangerous when combined with misconfigured "Copy Conditions" settings that improperly carried forward approval labels from previous code versions to new, malicious modifications.
 |
| GerriScary Vulnerability |
Most critically, researchers discovered they could exploit race conditions in Google's automated submission process.
By targeting code changes already approved with "Commit-Queue +2" labels, attackers could inject malicious code during the brief window before automated bots merged the changes into production repositories.
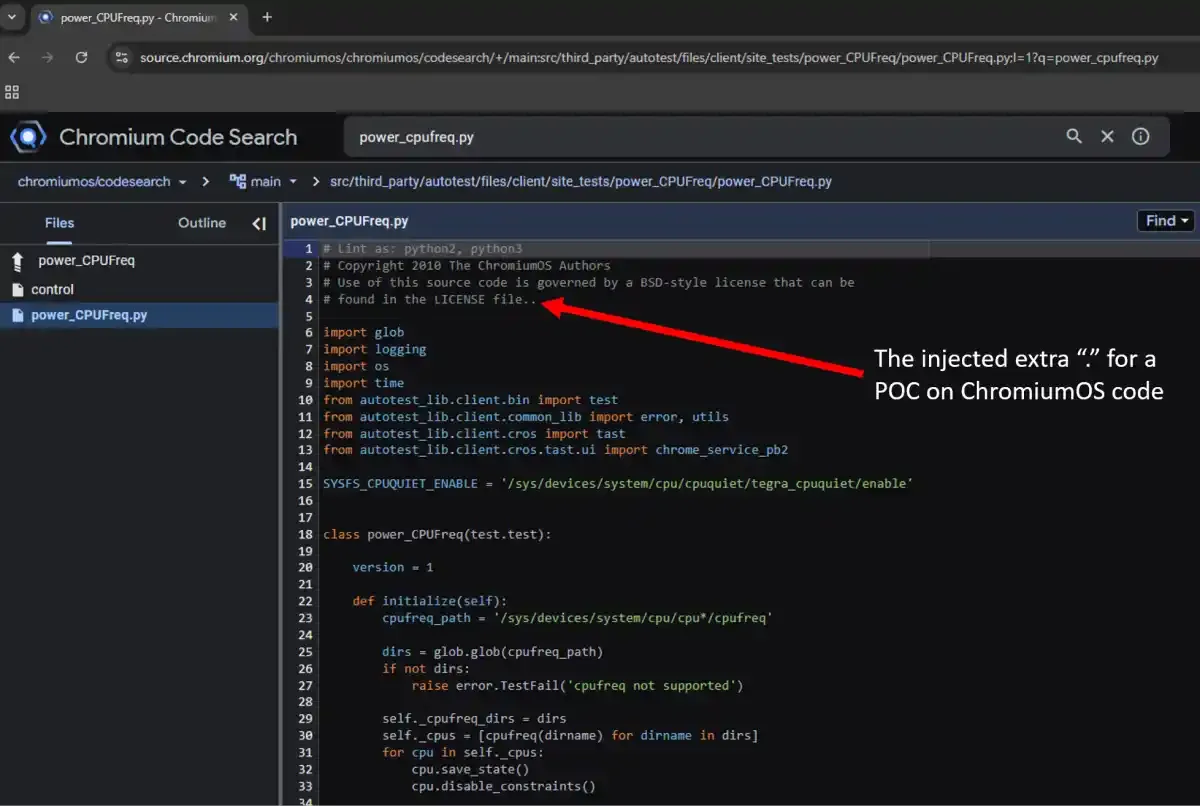 |
| GerriScary Vulnerability POC |
The researchers developed sophisticated scanning techniques to identify vulnerable projects without disrupting operations, using HTTP response fingerprinting to detect permission misconfigurations. Their proof-of-concept demonstrations successfully injected test code into ChromiumOS, validating the attack's feasibility across Google's infrastructure.
"The vulnerability allowed unauthorised code submission to at least 18 Google projects," Tenable's researchers explained, emphasising how the attack could have enabled large-scale supply chain compromises affecting millions of downstream users who rely on Google's software components.
Resolution and Industry Implications
Google has implemented comprehensive fixes across affected projects, modifying label-persistence configurations to require fresh code reviews for new patch sets and restricting the "addPatchSet" permission to trusted contributors only.
Organisations using Gerrit for their own projects should immediately audit their permission configurations and implement similar safeguards to prevent exploitation of these default settings that prioritise collaboration over security controls.